Abstract--
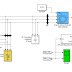
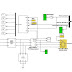
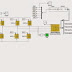
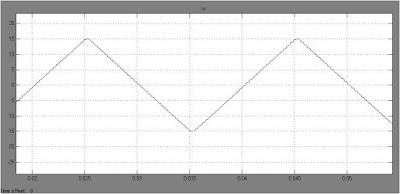
In this paper, a 3-phase induction motor model for simulation the field oriented control (FOC) system based on space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) is established in Ansoft/Simplorer software. The theory of field oriented control (FOC) and the principle of space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) were introduced. The simulation results are presented and analyzed. A Simulink simulation model of field oriented control system is presented as a comparison under the same conditions. The results indicated that the Simplorer model had quick response speed, small torque fluctuations and good performance both in steady and dynamic states. Furthermore, the Simplorer model can be coupled with the finite element model of the motor to achieve field-circuit coupling simulation of induction motor’s field oriented control system.
In this paper, a 3-phase induction motor model for simulation the field oriented control (FOC) system based on space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) is established in Ansoft/Simplorer software. The theory of field oriented control (FOC) and the principle of space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) were introduced. The simulation results are presented and analyzed. A Simulink simulation model of field oriented control system is presented as a comparison under the same conditions. The results indicated that the Simplorer model had quick response speed, small torque fluctuations and good performance both in steady and dynamic states. Furthermore, the Simplorer model can be coupled with the finite element model of the motor to achieve field-circuit coupling simulation of induction motor’s field oriented control system.