Abstract—
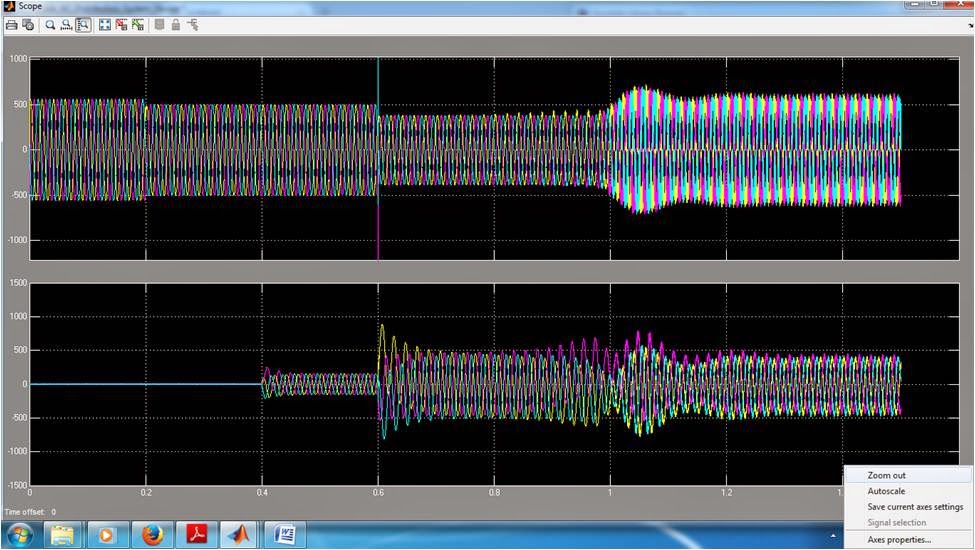
This paper presents a flexible ac distribution system device for microgrid applications. The device aims to improve the power quality and reliability of the overall power distribution system that the microgrid is connected to. The control design employs a new model predictive control algorithm which allows faster computational time for large power systems by optimizing the steady-state and the transient control problems separately. Extended Kalman filters are also employed for frequency tracking and to extract the harmonic spectra of the grid voltage and the load currents in the microgrid. The design concept is verified through different test case scenarios to demonstrate the capability of the proposed device and the results obtained are discussed.
This paper presents a flexible ac distribution system device for microgrid applications. The device aims to improve the power quality and reliability of the overall power distribution system that the microgrid is connected to. The control design employs a new model predictive control algorithm which allows faster computational time for large power systems by optimizing the steady-state and the transient control problems separately. Extended Kalman filters are also employed for frequency tracking and to extract the harmonic spectra of the grid voltage and the load currents in the microgrid. The design concept is verified through different test case scenarios to demonstrate the capability of the proposed device and the results obtained are discussed.