Abstract-
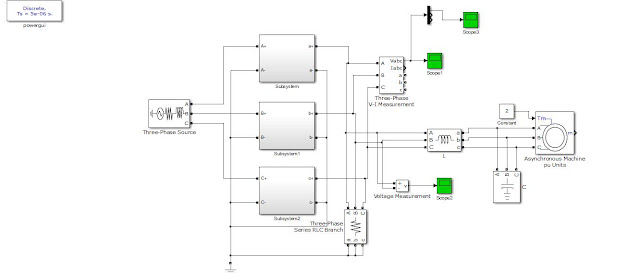
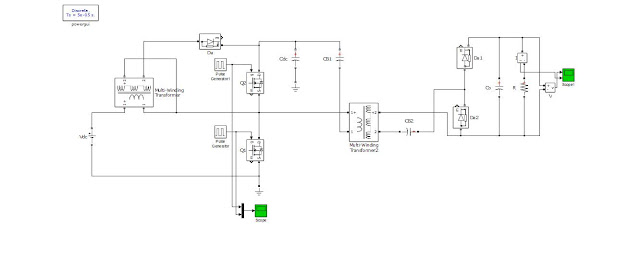
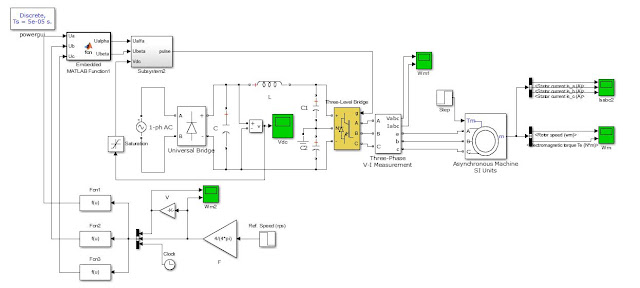
Power quality has become an important factor in power systems, for consumer and household appliances with proliferation of various electric and electronic equipment and computer systems. The main causes of a poor power quality are harmonic currents, poor power factor, supply-voltage variations, etc. A technique of achieving both active current distortion compensation, power factor correction and also mitigating the supply-voltage variation at the load side, is compensated by unique device of UPQC presented in this paper and this paper presents a modified synchronous-reference frame (SRF)-based control method to Shunt active filter and instantaneous PQ (IPQ) theory based control technique for series active filter to compensate power-quality (PQ) problems through a three-phase four-wire unified PQ conditioner (UPQC) under unbalanced and distorted load conditions. The proposed UPQC system can improve the power quality at the point of common coupling on power distribution systems under unbalanced and distorted load conditions. The simulation results based on Matlab/Simulink are discussed in detail in this paper.
Power quality has become an important factor in power systems, for consumer and household appliances with proliferation of various electric and electronic equipment and computer systems. The main causes of a poor power quality are harmonic currents, poor power factor, supply-voltage variations, etc. A technique of achieving both active current distortion compensation, power factor correction and also mitigating the supply-voltage variation at the load side, is compensated by unique device of UPQC presented in this paper and this paper presents a modified synchronous-reference frame (SRF)-based control method to Shunt active filter and instantaneous PQ (IPQ) theory based control technique for series active filter to compensate power-quality (PQ) problems through a three-phase four-wire unified PQ conditioner (UPQC) under unbalanced and distorted load conditions. The proposed UPQC system can improve the power quality at the point of common coupling on power distribution systems under unbalanced and distorted load conditions. The simulation results based on Matlab/Simulink are discussed in detail in this paper.