Abstract—
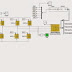
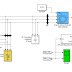
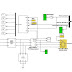
Flexible ac Transmission Systems (FACTS) devices are used to control power flow in the transmission grid to relieve congestion and limit loop flows. High cost and reliability concerns have limited the widespread deployment of FACTS solutions. This paper introduces the concept of Distributed FACTS (D-FACTS) as an alternative approach to realizing cost-effective power flow control. By way of example, a distributed series impedance (DSI) and a distributed static series compensator (DSSC) are shown that can be clipped on to an existing power line and can, dynamically and statically, change the impedance of the line so as to control power flow. Details of implementation and system impact are presented in the paper, along with experimental results.
Flexible ac Transmission Systems (FACTS) devices are used to control power flow in the transmission grid to relieve congestion and limit loop flows. High cost and reliability concerns have limited the widespread deployment of FACTS solutions. This paper introduces the concept of Distributed FACTS (D-FACTS) as an alternative approach to realizing cost-effective power flow control. By way of example, a distributed series impedance (DSI) and a distributed static series compensator (DSSC) are shown that can be clipped on to an existing power line and can, dynamically and statically, change the impedance of the line so as to control power flow. Details of implementation and system impact are presented in the paper, along with experimental results.