Abstract—
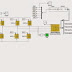
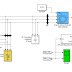
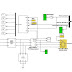
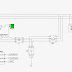
Renewable energy resources (RES) are being increasingly connected in distribution systems utilizing power electronic converters. This paper presents a novel control strategy for achieving maximum benefits from these grid-interfacing inverters when installed in 3-phase 4-wire distribution systems. The inverter is controlled to perform as a multi-function device by incorporating active power filter functionality. The inverter can thus be utilized as: 1) power converter to inject power generated from RES to the grid, and 2) shunt APF to compensate current unbalance, load current harmonics, load reactive power demand and load neutral current. All of these functions may be accomplished either individually or simultaneously. With such a control, the combination of grid-interfacing inverter and the 3-phase 4-wire linear/non-linear unbalanced load at point of common coupling appears as balanced linear load to the grid. This new control concept is demonstrated with extensive MATLAB/Simulink simulation studies and results.
Renewable energy resources (RES) are being increasingly connected in distribution systems utilizing power electronic converters. This paper presents a novel control strategy for achieving maximum benefits from these grid-interfacing inverters when installed in 3-phase 4-wire distribution systems. The inverter is controlled to perform as a multi-function device by incorporating active power filter functionality. The inverter can thus be utilized as: 1) power converter to inject power generated from RES to the grid, and 2) shunt APF to compensate current unbalance, load current harmonics, load reactive power demand and load neutral current. All of these functions may be accomplished either individually or simultaneously. With such a control, the combination of grid-interfacing inverter and the 3-phase 4-wire linear/non-linear unbalanced load at point of common coupling appears as balanced linear load to the grid. This new control concept is demonstrated with extensive MATLAB/Simulink simulation studies and results.