Abstract—
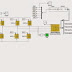
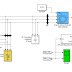
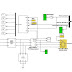
This paper examines voltage control of photovoltaic (PV) generators. Small PV generators are generally connected to service lines whose impedances are mostly resistive. Accordingly, it is hard to cancel voltage rise due to PV generation by changing power factor. This paper first proposes to insert a series reactor in a service line. Its value and effect are considered. Second, a combination of constant voltage control with unity power factor control is proposed to reduce line loss. The unity power factor control usually operates, but if the voltage exceeds an operating range, the constant voltage control starts. Two control block diagrams are drawn and rules for switching controls are derived. Some experimental results are demonstrated and compared with simulation results to verify its effectiveness.
This paper examines voltage control of photovoltaic (PV) generators. Small PV generators are generally connected to service lines whose impedances are mostly resistive. Accordingly, it is hard to cancel voltage rise due to PV generation by changing power factor. This paper first proposes to insert a series reactor in a service line. Its value and effect are considered. Second, a combination of constant voltage control with unity power factor control is proposed to reduce line loss. The unity power factor control usually operates, but if the voltage exceeds an operating range, the constant voltage control starts. Two control block diagrams are drawn and rules for switching controls are derived. Some experimental results are demonstrated and compared with simulation results to verify its effectiveness.