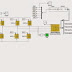
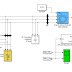
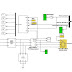
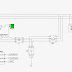
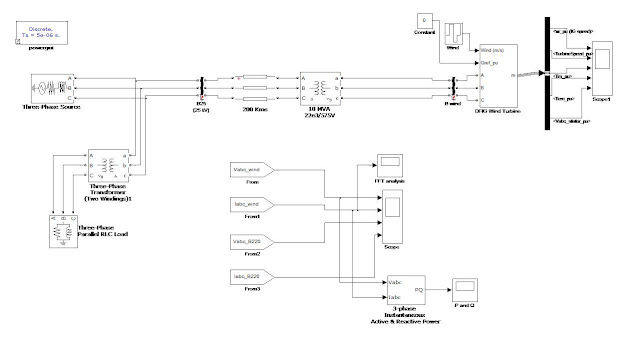
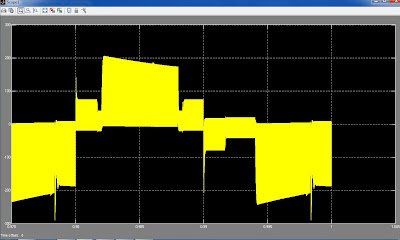
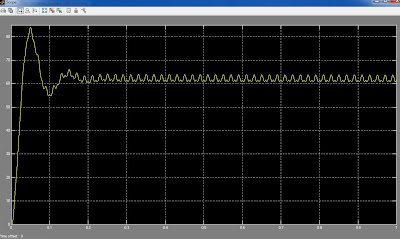
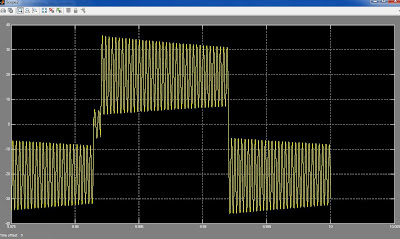
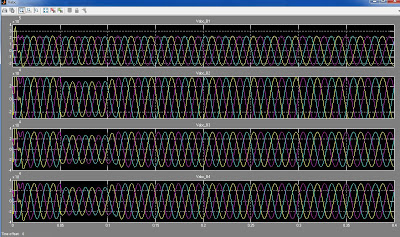
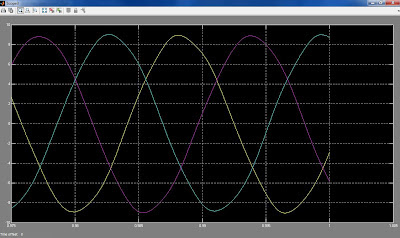
A photovoltaic array (PVA) simulation model to be
used in Matlab-Simulink GUI environment is developed and
presented in this paper. The model is developed using basic
circuit equations of the photovoltaic (PV) solar cells including the
effects of solar irradiation and temperature changes. The new
model was tested using a directly coupled dc load as well as ac
load via an inverter. Test and validation studies with proper load
matching circuits are simulated and results are presented here.
used in Matlab-Simulink GUI environment is developed and
presented in this paper. The model is developed using basic
circuit equations of the photovoltaic (PV) solar cells including the
effects of solar irradiation and temperature changes. The new
model was tested using a directly coupled dc load as well as ac
load via an inverter. Test and validation studies with proper load
matching circuits are simulated and results are presented here.