Abstract—
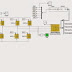
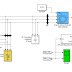
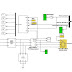
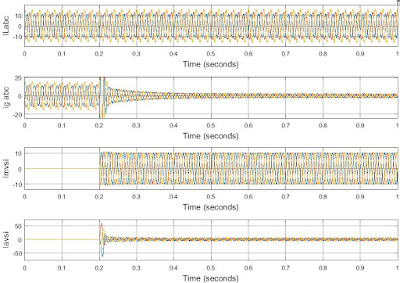
A quasi-Z-source boost dc–dc converter, which uses a switched capacitor, is proposed for fuel cell vehicles. The topology can obtain a high-voltage gain with a wide input-voltage range and requires only a low-voltage stress across each of the components. The performance of the proposed converter is compared with other converters which use Z-source networks. A scaled-down 400-V/400-W prototype is developed to validate the proposed technology. The respective variation in the output voltage is avoided when the wide variation in the input voltage happens, due to the PI controller in the voltage loop, and a maximum efficiency of 95.13% is measured.